Equations et inéquations : Exercice 13 première année secondaire
Activités numériques IActivités numériques IIActivités algébriquesFonctions linéairesEquations et inéquationsFonctions affinesSystème de deux équationsStatistiquesAnglesThalesRapports trigonométriqueVecteurs et translationsActivités dans un repereQuart de tourSections planes solideQCM
81 exercices
Exercice 13 --- (id : 1522)
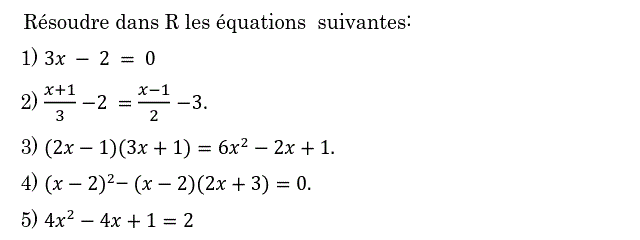
correction
1)
$3x-2=0$ $\iff 3x=2$
$\iff x=\frac{2}{3}$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{\dfrac{2}{3}}\right\}}$
$\iff x=\frac{2}{3}$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{\dfrac{2}{3}}\right\}}$
2)
$\frac{x+1}{3}-2=\frac{x-1}{2}-3$
$\iff\frac{x+1}{3}-\frac{x-1}{2}=-1$
$\iff \frac{2(x+1)}{6}-\frac{3(x-1)}{6}=-1$
$\iff \frac{2(x+1)-3(x-1)}{6}=-1$
$\iff 2(x+1)-3(x-1)=-6$
$\iff 2x+2-3x+3=-6$
$\iff 2x-3x=-6-2-3$
$\iff -x=-11$ $\iff x=11$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{11}\right\}}$
$\iff\frac{x+1}{3}-\frac{x-1}{2}=-1$
$\iff \frac{2(x+1)}{6}-\frac{3(x-1)}{6}=-1$
$\iff \frac{2(x+1)-3(x-1)}{6}=-1$
$\iff 2(x+1)-3(x-1)=-6$
$\iff 2x+2-3x+3=-6$
$\iff 2x-3x=-6-2-3$
$\iff -x=-11$ $\iff x=11$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{11}\right\}}$
3)
$(2x-1)(3x+1)=6x^2-2x+1$
$\iff \cancel{6x^2}+2x-3x-1=\cancel{6x^2}-2x+1$
$\iff 2x-3x+2x=1+1$
$\iff x=2$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{2}\right\}}$
$\iff \cancel{6x^2}+2x-3x-1=\cancel{6x^2}-2x+1$
$\iff 2x-3x+2x=1+1$
$\iff x=2$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{2}\right\}}$
4)
$(x-2)^2-(x-2)(2x+3)=0$
$\iff (x-2)[(x-2)-(2x+3)]=0$
$\iff (x-2)[x-2-2x-3]=0$
$\iff (x-2)(-x-5)=0$
$\iff x-2=0\; ou \; -x-5=0$
$\iff x=2 \; ou \; -x=5$
$\iff x=2 \; ou \; x=-5$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{-5;2}\right\}}$
$\iff (x-2)[(x-2)-(2x+3)]=0$
$\iff (x-2)[x-2-2x-3]=0$
$\iff (x-2)(-x-5)=0$
$\iff x-2=0\; ou \; -x-5=0$
$\iff x=2 \; ou \; -x=5$
$\iff x=2 \; ou \; x=-5$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{-5;2}\right\}}$
5)
$4x^2-4x+1=2$
$\iff (2x)^2-2\times (2x)\times 1+1^2=2$
$\iff (2x-1)^2=2$
$\iff (2x-1)^2-(\sqrt{2})^2=0$
$\iff (2x-1-\sqrt 2)(2x-1+\sqrt 2)=0$
$\iff 2x-1-\sqrt 2=0$ ou $2x-1+\sqrt 2=0$
$\iff 2x=1+\sqrt 2$ ou $2x=1-\sqrt 2$
$\iff x=\frac{1+\sqrt 2}{2}$ ou $x=\frac{1-\sqrt 2}{2}$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{\frac{1-\sqrt 2}{2};\frac{1+\sqrt 2}{2}}\right\}}$
$\iff (2x)^2-2\times (2x)\times 1+1^2=2$
$\iff (2x-1)^2=2$
$\iff (2x-1)^2-(\sqrt{2})^2=0$
$\iff (2x-1-\sqrt 2)(2x-1+\sqrt 2)=0$
$\iff 2x-1-\sqrt 2=0$ ou $2x-1+\sqrt 2=0$
$\iff 2x=1+\sqrt 2$ ou $2x=1-\sqrt 2$
$\iff x=\frac{1+\sqrt 2}{2}$ ou $x=\frac{1-\sqrt 2}{2}$
Donc $\boxed{S_\Bbb R=\left\{{\frac{1-\sqrt 2}{2};\frac{1+\sqrt 2}{2}}\right\}}$